
Wiesel, he won the won the Nobel Prize for his "split-brain" theory. In 1981, together with neuroscientist Torsten In the 1960s, neuroscientist Roger Sperry began to research the Little of both! Scientists and researchers have tried to answer this question right brain theories myth or fact? They actually are a
In the case of the dog, the movement of the legs will be under voluntary control, but the increased heartbeat and sweating will come under autonomic nervous control.Īre left brain vs. An example of the autonomic nervous system includes:. This happens due to the somatic nervous system that controls all the voluntary actions and the autonomic nervous system that controls all the involuntary actions. Now, the necessary action of running happens when the nervous system triggers the muscles and the body moves. If a dog is coming at you and you see it from a distance, the signal of sight generated is transmitted to the brain by the nervous system, and the information is processed. This process includes the reception of the signal and the processing of the response. Besides these small muscles, various glands release enzymes and hormones as a response activity of the nervous system. The most common reaction is the movement of muscles to generate the appropriate response via the nerves coming from the brain or the spinal cord until the muscles contract or relax. Deals with the response of the body, which the brain generates after receiving the sensations or stimuli. Similarly, on smelling a foul smell, the nerve in the nose gets stimulated and the sensation is converted into an electrical signal, which travels to the brain. These generate a signal that travels to the brain, and the necessary response from the motor neurons to remove the hand of the pan occurs. SENSORY SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM SKIN
On touching a hot pan, the sensation is received by the sensory neurons present on the skin of the hand.They are activated on the reception of a stimulus (any change in the external environment) and send impulses (electrochemical pulses) to the spinal cord and brain via nerves.The specialized nerve cells called receptors (which are part of neurotransmitters) are present all over the body.
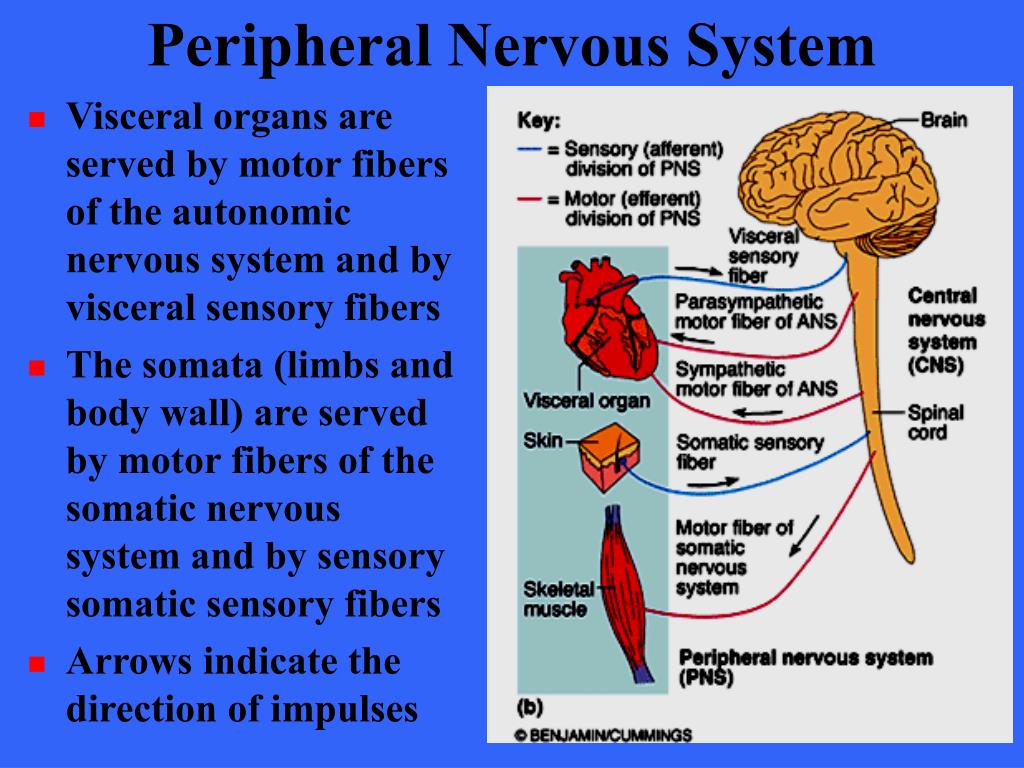
This is the reception of all the changes happening in the surroundings that are received by parts of the brain.Autonomic functions, which people cannot control, such as the beating of the heart.Somatic functions, which people can control voluntarily, such as blinking of the eyelids.These major functions can again be divided into two major categories.
Integration of sensory information from different parts of the body and processing them.Receiving and perceiving special sensations (taste, smell, vision, sounds).Reception of general sensory information (touch, pressure, temperature, pain, vibration).The 4 main functions of the nervous system are: Here are the 4 main functions of the nervous system.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
